In a recent series of articles on ECS, I described a methodology for provisioning and deploying a test FastAPI application on AWS ECS.
One of the more difficult aspects of it is handling database migrations. When and how should the migrations be run when deploying onto ECS? Do we run it as part of the service deployment or as a separate task?
My personal preference is to run database migration as a separate task. This would decouple the handling of database migrations as a separate operation. While it is possible to create a single task definition with the migration task running as a container before the service container starts, I always feel that this is an anti-pattern. What happens if the database migration takes a long time due to the size of the database? The service deployment would need to wait, resulting in poor feedback loop.
After some trial and error I came up with the following approach, which consists of 2 stages:
-
Running a ECS task for the database migration during initial setup.
-
Creating a lambda to run the database migration for deployment workflows.
Running database migration during setup
When setting up the infrastructure via terraform, we create a one-off task via aws cli:
# Run one-off db migration task
locals {
config = {
"awsvpcConfiguration" : {
"subnets" : var.private_subnets,
"securityGroups" : [var.ecs_service_sg],
}
}
overrides = {
"containerOverrides" : [
{
"name" : "fastapi",
"command" : ["alembic", "upgrade", "head"]
}
]
}
}
resource "terraform_data" "create_migration_task" {
depends_on = [aws_iam_role.task_execution_role]
# Create task definition from template with secrets ARN from secrets manager
provisioner "local-exec" {
command = "TASK_ID=$(aws ecs run-task --cluster ${var.cluster_name} --task-definition ${data.aws_ecs_task_definition.fastapi.arn} --network-configuration '${jsonencode(local.config)}' --overrides '${jsonencode(local.overrides)}' | jq -r '.tasks[0].taskArn') && aws ecs wait tasks-stopped --cluster ${var.cluster_name} --tasks $TASK_ID"
}
}The terraform_data resource calls ecs run-task to invoke the database migration. It overrides the application container image command with a call to alembic. It requires the network configuration to be specified together with the container overrides. We wait for the task to stop before proceeding to provision the initial application service and code deploy resources.
Database migration lambda
To run the database migration after provisioning, I created a separate lambda which gets invoked via a custom EventBridge rule. This would run a standalone ECS task to perform the database migration when required. By using an event-driven approach, we can run the database migration when we choose to, so long as we create the right event to put on the Event Bus.
For this example, I use the default event bus.
The rule I created is called run-database-migration and has the following event pattern:
{
"Source": "ecs.migration",
"DetailType": "AWS ECS Migration Task",
"Detail": "{\"taskdef_arn\": \"<TASK DEF ARN>\"}"
}It has a source of ecs.migration and a detail type of ECS migration task. It has a reference to the latest task definition which will be used by the lambda code to run a migration task.
In my terraform resource files, I created the following lambda resources:
data "archive_file" "lambda_migration" {
type = "zip"
source_file = "${path.module}/lambda_migration.py"
output_path = "/tmp/lambda_migration.zip"
}
resource "aws_lambda_function" "lambda_migration" {
filename = "/tmp/lambda_migration.zip"
function_name = "DatabaseMigration"
role = aws_iam_role.database_migration.arn
handler = "lambda_migration.lambda_handler"
runtime = "python3.12"
depends_on = [aws_iam_role.database_migration]
timeout = 900
source_code_hash = data.archive_file.lambda_migration.output_base64sha256
environment {
variables = {
PRIVATE_SUBNETS = jsonencode(var.private_subnets)
SECURITY_GROUP = var.ecs_service_sg
CLUSTER_NAME = var.cluster_name
}
}
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_log_group" "lambda_migration" {
name = "/aws/lambda/${aws_lambda_function.lambda_migration.function_name}"
retention_in_days = 30
}
# Create eventbridge rule
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_rule" "migration" {
name = "run-database-migration"
description = "Runs a one-off DB migration task in ECS cluster"
event_pattern = jsonencode({
detail-type = [
"AWS ECS Migration Task"
]
source = ["ecs.migration"]
})
}
resource "aws_cloudwatch_event_target" "migration" {
rule = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.migration.name
target_id = aws_lambda_function.lambda_migration.id
arn = aws_lambda_function.lambda_migration.arn
}
# Below is required else the trigger doesn't show up in the lambda config...
resource "aws_lambda_permission" "allow_eventbridge" {
statement_id = "AllowExecutionFromCloudWatch"
action = "lambda:InvokeFunction"
function_name = aws_lambda_function.lambda_migration.function_name
principal = "events.amazonaws.com"
source_arn = aws_cloudwatch_event_rule.migration.arn
}The HCL code above defines the lambda which calls the migration task. It’s triggered by a custom event rule defined by aws_cloudwatch_event_rule. The event target resource links the rule to the lambda. In the console, we can link the event rule either via the lambda configuration or by editing the event rule. Here, we need to define a resource of aws_lambda_permission to link a custom rule to the lambda. The private subnets, security group used by the API service and cluster name are set as environment variables on the lambda.
The lambda code parses the event and uses it to run a one-off ECS task:
import os
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
if event['detail-type'] == "AWS ECS Migration Task" and event['source'] == 'ecs.migration':
private_subnets = json.loads(os.getenv("PRIVATE_SUBNETS"))
security_group = os.getenv("SECURITY_GROUP")
cluster_name = os.getenv("CLUSTER_NAME")
network_config = {
"awsvpcConfiguration": {
"subnets": private_subnets,
"securityGroups": [security_group]
}
}
overrides = {
"containerOverrides": [{
"name": "fastapi",
"command": ["alembic", "upgrade", "head"]
}]
}
client = boto3.client('ecs')
response = client.run_task(
cluster=cluster_name,
taskDefinition=event['detail']['taskdef_arn'],
networkConfiguration=network_config,
overrides=overrides,
startedBy='ecs.migration'
)
status = {'statusCode': 200, 'body': json.dumps('Ran migrtion task')}
else:
status = {
'statusCode': 400,
'body': json.dumps('Event not matching ECS Migration task')
}
return statusIn the lambda, we use the ecs client to run a task whereby we use the same image as the application but override the command to run alembic upgrade head. In run_task, we added the additional tag of startedBy so we can query for the migration task status. I have bundled the database migration files when building the application container image. We can check the cloudwatch logs to ensure that the migration has run successfully.
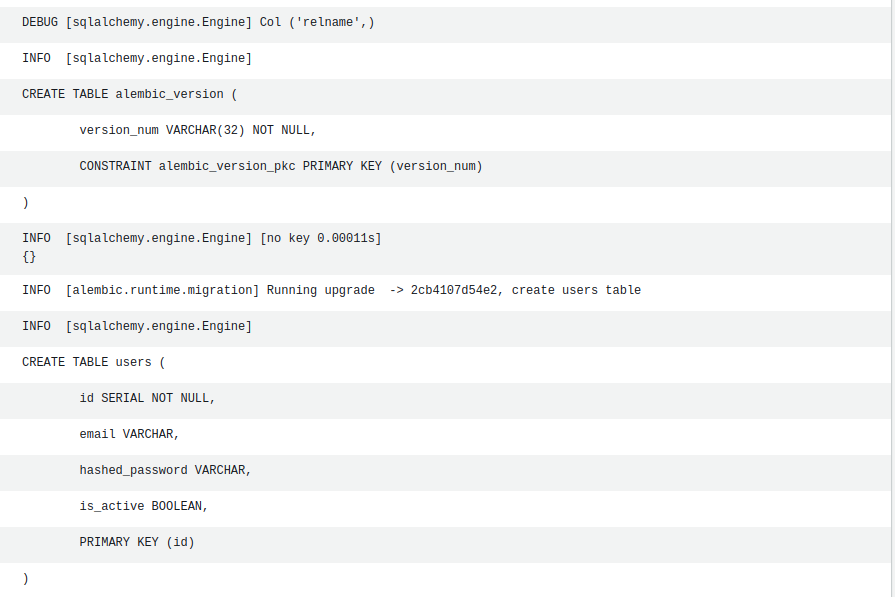
Deployment Pipeline
In the github deployment workflow, to ensure that the latest database migrations are applied, we build the new image as normal since the migration files are bundled with the application container.
During the deployment stage, we add an additional stage of running the migration before deploying the new task definition via code deploy:
- name: Run database migration
run: |
./.github/events.sh $ migration.json
# Put message on eventbus
aws events put-events --entries file://migration.json
sleep 10
# Wait for task to finish?
tasks=$(aws ecs list-tasks --cluster $ --started-by 'ecs.migration' --query 'taskArns' --output text)
echo "Waiting for migration tasks to complete..."
echo ${tasks}
aws ecs wait tasks-stopped --cluster $ --tasks $tasksThe events.sh script takes as parameters the task definition name and the output event json file to pass to put-events. It sleeps for 10 seconds after which we query for tasks with the ecs.migration started by tag and wait for the tasks to stop before we proceed to the code deploy stage.
The events.sh script replaces the detail body of the event with the task definition arn from a template:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -e
echo "Creating database migration event..."
TASK_DEF=$1
OUTPUT=$2
TASK_ARN=$(aws ecs describe-task-definition --task-definition ${TASK_DEF} | jq '.taskDefinition.taskDefinitionArn')
echo $TASK_ARN
details="{\"taskdef_arn\": ${TASK_ARN}}"
jq --arg details "$details" '.[0].Detail = ($details | tostring)' .github/database_migration.json > $OUTPUT
cat $OUTPUTTo run the migration manually, you can also create an event with the matching attributes in the console or the CLI. Below is a screenshot of invoking the lambda via the EventBridge send events:
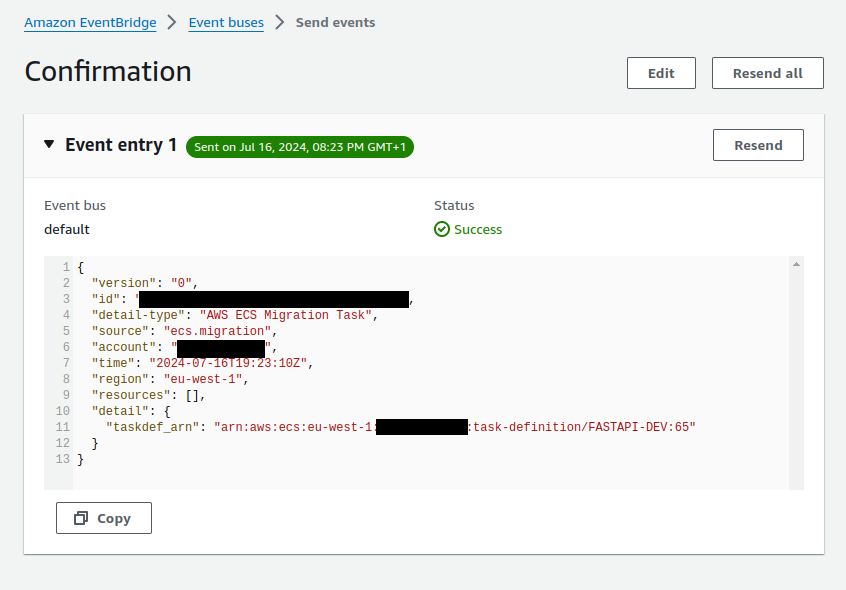
With the following setup, I was able to successfully run database migration